Precision Farming at a Glance: Guide to E-Agriculture

- What is digital agriculture?
- What is precision farming?
- What is the difference between traditional farming and modern farming approaches?
- Big data in precision agriculture and precision farming technology
- How does precision farming work?
- How to start precision farming?
- Essentials of precision agriculture technology
- Precision farming solutions & technologies
- Precision agriculture for sustainability and environmental protection
Tech farming, site-specific crop management, farming by satellite, precision farming technology, and many other terms related to digital agriculture make people feel on pins and needles as they bring a complete revolution to the whole agriculture industry.
Although it is a hard pill to swallow, hunger remains a huge problem of modern reality, making millions of people suffer from a lack of food. The reason for that is the discrepancy between the pace of agricultural development and the rate of population, which means that the agri-food industry requires innovation and complete digitalization to handle the demands of the constantly growing population.
Here the concept of precision agriculture or precision farming is a notably valuable solution to optimize agriculture practices and improve collective farming. Therefore, we would like to reveal the topic of precision ag in this no-nonsense intro guide.
What is digital agriculture?
Digital agriculture, smart farming, or e-agriculture is the practice of employing innovative technologies and tools to help farmers advance the entire agri-food value chain and achieve better results in food production.
As a fully data-backed concept, digital agriculture offers solid principles that can be utilized in crop farming, meat and dairy business, food processing, horticulture, and more. In a nutshell, digital agriculture companies aim to automate manual labor and optimize various farming processes to obtain complete control, traceability, and sustainability.
What is precision farming?
Precision farming (PF), satellite farming, or precision agriculture is a series of GIS-based technologies designed explicitly for stock-traded cash crops. In this precision farming definition, the GIS-based indicates technologies that help provide all the data with relevant coordinates on the field.
Precision farming or precision agriculture technology means site-specific crop management allowing stakeholders and farmers to significantly increase the profitability of each land parcel across the field.
In simple terms, with precision farming technology, every field you manage is divided into separate productivity zones with individual service and maintenance practices, which help ensure proper plant development.
What is the difference between traditional farming and modern farming approaches?
There are old and new approaches with certain essentials to discuss when it comes to agriculture and farming. In essence, the old school approach uses the entire field as a single unit to be managed and optimized, while the new school data-driven approach makes each plant a fully traceable part of your field.
The old-school approach covering primitive farming methods is based on the size of the whole field with an equal spread of chemicals and seeds, ignoring the differences of specific territories. Also, read about AI in warehouse management.
Even though such a traditional farming approach is easy to implement, complete unification becomes troublesome due to resource wastage, quality issues, and yield losses. Thus, you skate on thin ice as you need to deal with additional crop calibration and cleaning as well as harvest over-ripening.

Meanwhile, the new school farming approach provides total control over each land parcel on the field, so you can manage high-productive and low-productive field zones separately. This modern farming approach refers to precision farming or precision ag and allows you to maintain the finest quality of yield. The precision farming technology helps to reduce total agriculture business costs, including logistics operations, by 20%. That’s why modern farming has become a new traceability trend in the supply chain for vegetables and fruits.
Thus, you can use more seeds and fertilizers on fruitful field areas to obtain enhanced harvesting and, at the same time, reduce seeds and chemicals for further use on field zones with lower fertility.
As a result, you get superior soil, not depleted due to proper maintenance, optimized plant growing conditions, excellent grade of yield, and cost-efficiency. Furthermore, by employing precision agriculture for the development of your production, you can take advantage of the full potential of your land, which is highly beneficial for agribusinesses.
Big data in precision agriculture and precision farming technology
Switching from field to plant, all smart data, forming the modern revolution in agriculture, and other fundamental principles of precision farming, also known as farming by satellite, are not feasible without big data.
The thing is that precision agriculture technology is an entirely data-backed solution that depends on four essential data sources. Moreover, before the actual decision-making and technology implementation, all the information here goes through the following critical stages:
- Data collection,
- Data storage,
- Data processing,
- Data visualization.
When it comes to precision ag data sources, it is essential to consider manual input data, field operations data, sensor data related to weathering and soil, and remote sensing data. Thus, manual input data denote information that should be entered manually with no automation, such as crop hybrid names or laboratory test results, etc.
Field operations data can be gathered automatically right from the compatible field equipment. This type of information covers seeding density, the speed of operations, the applied pesticides, and more. As for the sensor data, this data source helps define the exact conditions of particular fields and can be obtained from weather stations and various soil and handheld sensors.
Remote sensing data is an informative free data source that doesn’t require any additional equipment. You can collect such data with the help of drones and satellites. Keep in mind that all data sources are crucial for a correct precision farming workflow.
How does precision farming work?
Precision farming or precision agriculture technology includes a range of sophisticated processes divided into three fundamental levels — GIS software, GPS guidance, and VRA, a variable rate application. The basic level of satellite farming comes in GIS software that allows gathering all the information about spatial differences and disparities of the field from satellites, drones, soil mapping, field sensors, and more.
Then GPS guidance takes place. This level of precise ag processes provides accurate field operations placement and enables the data collection from field equipment concerning a specific geographic position. The opportunity to set autopilot or parallel steering driving is the peculiarity of GPS guidance.
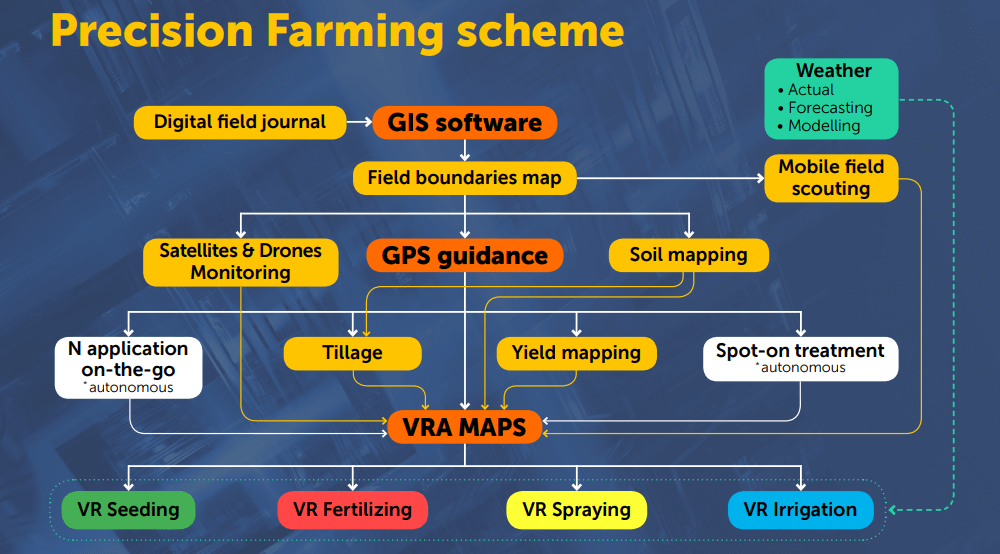
Another inherent level of precise farming technology is a variable rate application (VRA). The VRA maps utilize all the information collected from previously mentioned operations, making it possible to change inputs. Such an addition allows for the use of the full potential of each land parcel.
Moreover, variable rate application consists of VR seeding, VR fertilizing, VR spraying, and VR irrigation. These components help to fully control seeding density, chemicals dosage, and water applied, taking into account varied parameters of the soil. Additionally, to boost the results of VRA operations, you can also take advantage of local weather data.
How to start precision farming?
As far as precision farming represents a complex technology with a diversity of tools, operations, and processes, the integration of precision agriculture requires a smooth, step-by-step digitalization.
First and foremost, make sure you understand the principles of the VRA and the supplementary technologies it requires for a stable and high-productive workflow. All the technologies are crucial as they perform as a whole, allowing you to arrange and control particular parameters for your harvest and fields.
Then focus on inputting your data into a related software for farm management. It will help you put things in order and better understand your fields and their essentials. Once you enter all the information, pay attention to several services for field mapping, such as crop metrics, soil conditions, vegetation dynamics, and more. These integrations allow you to get valuable data insights about the productivity zones in your fields.
The next step is acquiring GPS guidance. It allows you to bring your field operations to the next level as you can fill in the gaps, work without any interruptions, and minimize the chances of human errors. Furthermore, the implementation of GPS guidance facilitates further VRA implementation, which is the most profound part of precision farming technology, allowing you to control every pixel of your land efficiently.
Essentials of precision agriculture technology
The primary principle of precision agriculture technology is the principle of pixel optimization which considers the field’s measured parameters and separate maintenance of every pixel of land. Thus, when it comes to precision farming, resolution matters a lot and directly affects decision-making.
Fortunately, since 2016 access to 10m data from Sentinel satellites has been available for free. For sure, there is a range of paid options that can provide supreme imagery with a precision of up to 30cm.
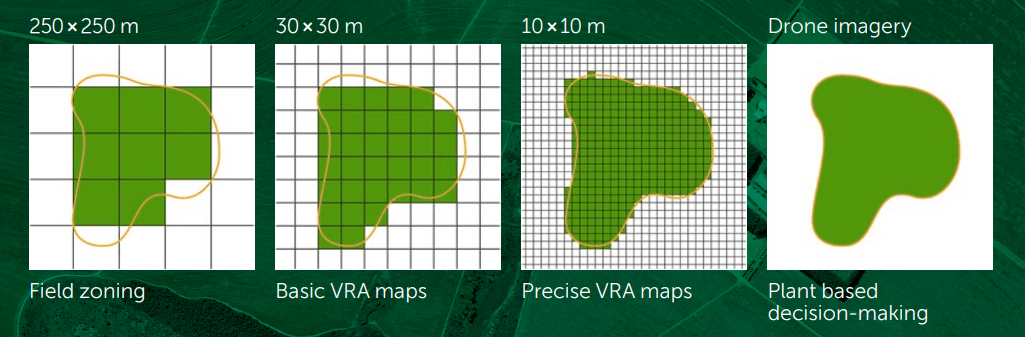
Here the only con is that clouds interfere with satellites, so the imagery is problematic when the weather is cloudy. Nevertheless, in such a situation, drones come as a great alternative to satellites as they can fly under the clouds delivering excellent images in a high resolution.
Additionally, keep in mind that the precision of VRA equipment defines the size of the pixel. Therefore, whether it is a distribution unit control, equipment section control, or a full working width application control, you can determine the actual pixel size of the particular field with the help of technology with the lowest resolution applied.
Precision farming solutions & technologies
Site-specific crop management or precision agriculture brings tons of excellent opportunities for businesses. Thus, there are precision farming service companies covering the needs of those who can’t buy specialized equipment for some reason. Among other precision farming solutions, you definitely should pay attention to monitoring soil carbon sequestration as precision ag data provides exhaustive information on CO2 to monetize your fields.
As for precision farming technologies, tractors powered by electricity and hydrogen have a vast potential and can deliver even more efficiency to the precision ag. Moreover, drone swarms and small robots are great for replacing heavy machinery in fields and transforming field operations, making them far more ecological and flexible.
Precision agriculture for sustainability and environmental protection
Sustainability and environmental friendliness are crucial aspects to consider, especially when it comes to business. Precision farming or farming by satellite aims to transform the entire agriculture industry with a positive impact on the environment.
Thus, the approach of precision agriculture for sustainability and environmental protection can help us maintain the best quality of the soil, lower water & soil pollution, decrease emissions of CO2, cut chemical pressure, and much more. Satellite farming is entirely eco-friendly, allowing you to take care of the environment and emphasize your brand image. That’s how humanity engaged in calculating carbon footprint and CO2 reduction.
To conclude, precision agriculture technology helps achieve comprehensive resource planning and utilization, informed decision-making, better harvesting, exceptional quality of yield, and constantly growing profitability. With precision farming, you save plenty of time and money as every land parcel of your fields becomes fully manageable and traceable on a plant-based level.
Coreteka AgriFood team is capable of providing a competent piece of advice regarding building precision farming software tailored to your needs. We carefully analyze your project requirements and find the most efficient solution, to solving your business challenges.
Also, you can read an interesting article “What is vaccine inventory management software”.
If you are looking for a professional team to build software for your agricultural business, contact us!


 Category:
Category:  Tags:
Tags: 

